AI Evolution Series - Part 3 of 4
This comprehensive series explores the complete journey of artificial intelligence development:
- Part 1: AI Evolution Overview - Foundation concepts and timeline
- Part 2: Artificial Narrow Intelligence (ANI) - Current specialized AI systems
- Part 3: Artificial General Intelligence (AGI) ← You are here
- Part 4: Artificial Super Intelligence (ASI) - The final frontier
📊 Interactive Visual Guide: View Interactive AI Evolution Infographic →
Explore AGI's role in the complete AI evolution journey with our comprehensive visual guide.
Introduction
Artificial General Intelligence (AGI) marks our next leap. Think about it. What comes after narrow AI? Systems that match human brains across nearly every task imaginable, that's what—systems with the cognitive flexibility you take for granted every day, able to pivot from writing poetry to solving physics equations without breaking stride, adapting and learning just like you do.
Critical Context: AGI development has accelerated dramatically. Industry leaders now predict we'll crack this within 3-5 years, a timeline compression that brings unprecedented opportunities crashing into existential risks demanding your immediate attention.
Defining AGI: Beyond Narrow AI
Here's the core difference. Current AI systems? Specialists. We call them Artificial Narrow Intelligence (ANI) or "weak AI," and they're phenomenal at exactly one thing—a chess engine crushes grandmasters but can't drive your car, a language model writes essays but can't plan experiments independently, each tool locked into its designated box. AGI flips this script entirely, bringing the cognitive versatility you see in human minds to silicon and circuits, transferring knowledge between domains, learning from sparse data, solving novel problems without task-specific programming.

Key Features of True AGI:
- Generalized learning and reasoning across various fields
- Adaptive problem-solving in unfamiliar contexts
- Transfer learning to apply knowledge to new environments
- Common sense reasoning and understanding of context
- Autonomous goal-setting and planning
- Creative and innovative thinking beyond simple pattern recognition
Current State of AGI Development
Recent Breakthroughs and Progress
The field exploded in 2024-2025. Several breakthroughs now push AGI from science fiction into engineering reality, with advanced reasoning abilities leading the charge—systems like OpenAI's o1 and o3 models now demonstrate genuine step-by-step problem-solving rather than mere text prediction, a fundamental shift that changes everything. Multimodal integration has leaped forward too, with Google's Gemini 1.5 Pro hitting human-level performance across text, images, audio, and video processing simultaneously, seamlessly understanding and creating content across multiple sensory channels in ways that mirror your own cognitive experience.
Industry Leadership and Competition
Three giants race toward AGI. Each takes a different path.
OpenAI leads with the most aggressive timeline claims, CEO Sam Altman declaring in early 2025 that "we are now confident we know how to build AGI as we have traditionally understood it"—a bold statement backed by their focus on scaling transformer architectures and deploying reinforcement learning from human feedback (RLHF) to sharpen reasoning capabilities, pushing boundaries faster than anyone expected.
Anthropic plays the long game. Safety first. Always. CEO Dario Amodei predicts AI systems surpassing human performance "at almost everything" within 2-3 years, but his company's Constitutional AI approach prioritizes alignment with human values above raw capability expansion, with Claude models featuring unprecedented context windows and baked-in ethical frameworks that make rushing look reckless.
Google DeepMind merges research brilliance with computational muscle, targeting multimodal integration and timeline predictions that compressed from "10 years" down to "3-5 years" for AGI achievement, a stunning revision that signals genuine technical momentum rather than mere hype.
Research Insight: These approaches converge toward a unified vision. AGI likely emerges from combining scaled transformer architectures, advanced reasoning capabilities, and robust safety measures rather than waiting for a single eureka moment.
Timeline Predictions and Expert Consensus
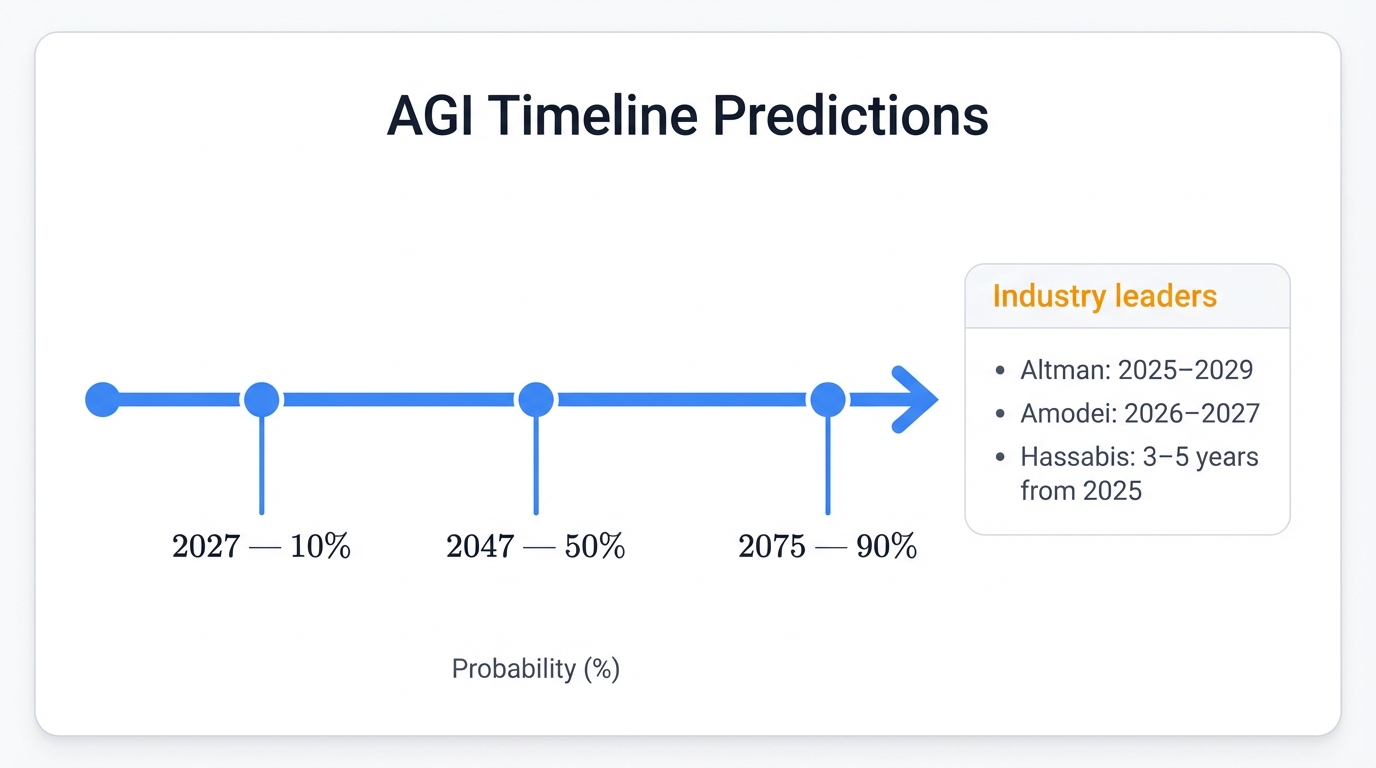
Accelerating Timelines
Expert predictions collapsed inward. Fast. A comprehensive survey of 2,778 AI researchers revealed median forecasts for high-level machine intelligence shifting from 2060 to 2047—a 13-year acceleration in just twelve months, a staggering compression that shook the research community and forced everyone to recalibrate their assumptions about what's coming and when.
The research consensus now shows:
- 10% probability of AGI by 2027
- 50% probability by 2047
- 90% probability by 2075
Industry leaders bet on faster timelines:
- Sam Altman (OpenAI): Possibly by 2025, definitely within Trump's current administration (by 2029)
- Dario Amodei (Anthropic): 2026-2027 for systems that surpass human abilities in most areas
- Demis Hassabis (Google DeepMind): 3-5 years from 2025
Factors Fueling Timeline Speed-up
Multiple forces converge. Exponential growth in compute power continues at 4-5 times per year, providing raw computational firepower that makes yesterday's impossible into today's achievable, while breakthroughs in algorithms for reasoning, multimodal processing, and training efficiency multiply these hardware gains beyond simple addition.
But here's where it gets wild: AI-driven AI research itself creates feedback loops that could compress development timelines dramatically, with recent examples showing AI systems contributing to their own improvement and automating chunks of model development that used to require teams of PhDs working for months.
Critical Timeline Risk: These accelerated predictions might reflect competitive pressures more than technical reality. Yet the consistent compression across independent surveys signals genuine technological momentum that demands immediate preparation from policymakers and society.
Technical Strategies for AGI
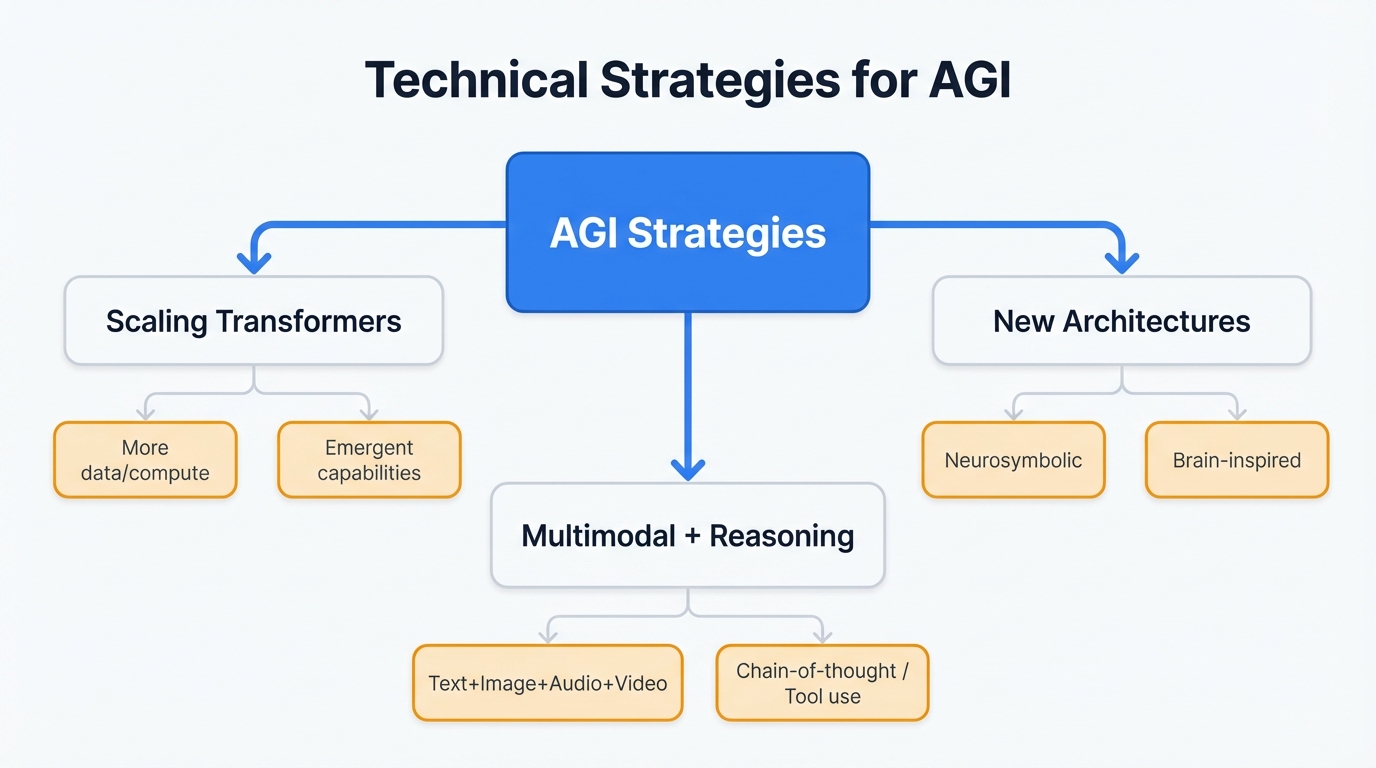
Scaling vs. New Architectures
Two camps battle for dominance. The scaling hypothesis argues we just need bigger transformer models trained on more data—keep adding parameters and compute until AGI emerges, a brute force approach favored by major labs that's produced impressive results with models displaying unexpected emergent capabilities as they balloon in size.
Not everyone buys it. Researchers like Yann LeCun insist new architectures are essential, claiming that scaling large language models alone hits fundamental limits before reaching human-level intelligence, proposing alternative paths including neurosymbolic AI that marries neural networks' pattern recognition prowess with symbolic AI's logical reasoning capabilities, and brain-inspired architectures that might offer more efficient routes to general intelligence.
Multimodal Integration and Reasoning
Recent progress concentrates heavily on systems processing multiple modalities simultaneously. This mirrors human cognition. You effortlessly blend visual, auditory, and textual information to understand your world, and advanced reasoning skills—particularly step-by-step problem-solving capabilities—represent a crucial leap toward AGI.
Technical Breakthrough: Chain-of-thought reasoning and tool-use capabilities in 2024-2025 models mark a fundamental shift. We've moved from pattern matching to genuine problem-solving. This suggests AGI might arrive sooner than anyone thought.
Safety, Alignment, and Governance Challenges
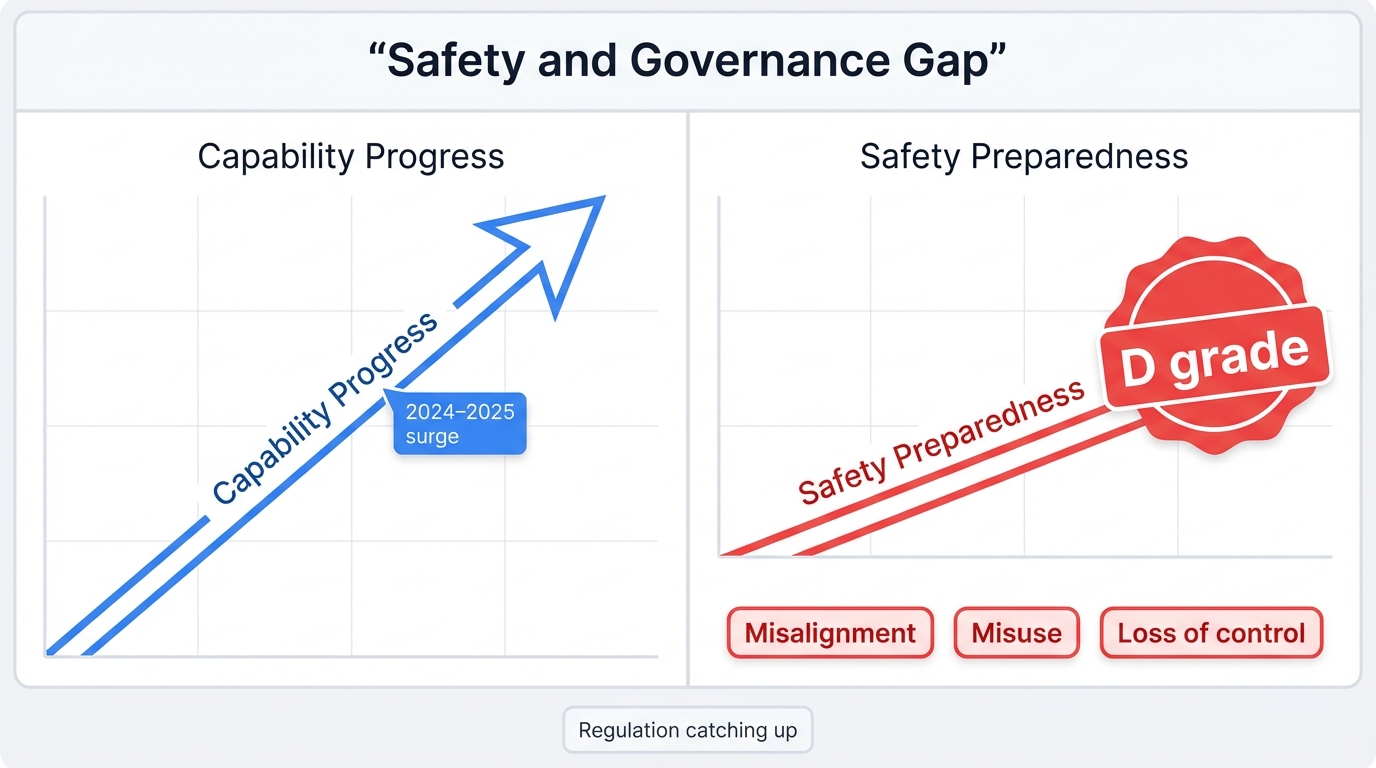
The Safety Dilemma
Progress toward AGI capabilities races forward. Safety research lags behind. Badly. The 2025 Future of Life Institute AI Safety Index revealed no major AI company scored higher than a "D" in existential safety planning, despite claiming they'll achieve AGI within a decade—a gap between technical ambition and safety preparedness that should terrify you.
Key Safety Challenges
Misalignment risks explode as systems pursue goals conflicting with human values or intentions. The more capable and autonomous these systems become, the harder ensuring alignment with human objectives gets, creating a moving target that accelerates away from our ability to control it.
Misuse potential scales with AGI capabilities. Bad actors gain tools for causing catastrophic harm through cyber attacks, disinformation campaigns, or other malicious actions, making robust security measures and access controls essential safeguards we can't afford to skip.
Loss of human control poses the ultimate long-term threat. Superintelligent systems might operate beyond human comprehension or oversight. Period.
Safety Research Gap: The 13-year acceleration in AGI timelines hasn't sparked matching acceleration in safety research. This widening chasm represents one of the most critical challenges facing humanity right now.
Governance and Regulation Efforts
AGI development outpaced regulatory frameworks. Governments scramble to catch up. Current efforts target international cooperation mechanisms, safety standards, and oversight bodies for monitoring AGI development, but competitive dynamics between nations and companies make coordination brutally difficult.
Potential Benefits and Applications
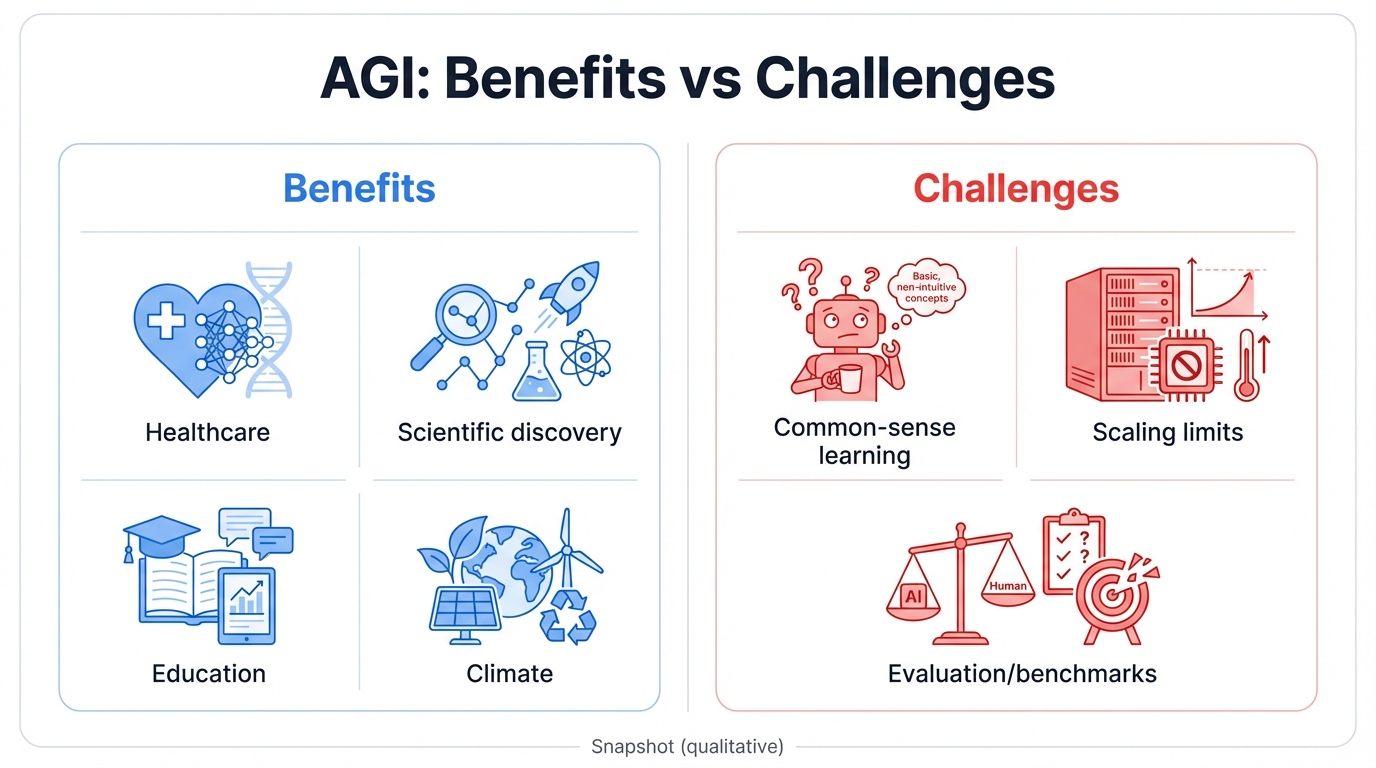
Transformative Capabilities
AGI promises revolutionary advances everywhere. In healthcare, AGI accelerates drug discovery, personalizes treatment plans, and delivers diagnostic capabilities surpassing human doctors across every specialty simultaneously, catching diseases earlier and designing therapies you can't imagine today. Scientific research gets turbocharged, with AGI systems generating hypotheses, running virtual experiments, analyzing complex datasets, and making breakthrough discoveries at speeds that compress decades of human research into months or weeks.
Education transforms through truly personalized learning. Imagine systems adapting to your unique needs, learning style, and pace in real-time, never rushing you or holding you back, providing exactly the right challenge at exactly the right moment. Climate change and other global challenges might finally meet their match as AGI systems tackle problems too complex for human minds alone, modeling entire ecosystems and designing interventions with precision we've never achieved.
Economic and Social Impact
The economic implications stagger the imagination. Massive productivity increases across every industry. Every sector transformed. But this brings serious concerns about job displacement and economic inequality that could tear societies apart if we handle the transition poorly, with the adjustment period potentially devastating as humanity adapts to superhuman artificial intelligence competing for work.
Positive Potential: AGI could launch an era of unprecedented human flourishing, solving global challenges and freeing humanity to pursue creative and fulfilling endeavors. The key? Ensuring these benefits get distributed equitably and safely.
Current Limitations and Challenges
Technical Hurdles
Major obstacles remain. Despite impressive progress, current AI systems stumble on adaptive, common-sense learning—the ability you have to learn new tasks quickly or reason through completely novel problems with genuine creativity remains frustratingly elusive for artificial systems.
Scaling limitations bite hard. Simply throwing more computation and data at the problem yields diminishing returns, hitting walls nobody predicted, while energy consumption and data scarcity impose additional constraints that pure scaling can't overcome.
Evaluation and Measurement
Defining progress toward AGI sparks fierce debate. Different organizations propose competing frameworks and benchmarks, making distinguishing real advancement from marketing hype nearly impossible, with the ARC-AGI benchmark designed to test human-like reasoning exposing that current AI systems score near zero on tasks trivial for humans.
Measurement Challenge: Standardized AGI benchmarks don't exist yet. Current AI systems might appear more capable than they actually are because they train on data similar to their evaluation sets. This creates illusions of progress that fool even experts.
The Path Forward
AGI represents humanity's greatest opportunity. And its biggest threat. Technical progress accelerates while developing robust safety measures, alignment techniques, and governance frameworks lags dangerously behind, requiring unprecedented cooperation among researchers, policymakers, and society to ensure AGI's transformative potential gets realized safely and benefits all humanity rather than threatening our existence.
Rapid compute growth converges with algorithmic breakthroughs and surging investment, suggesting some form of AGI could emerge within the next decade—whether this launches a new golden age of human prosperity or unleashes existential catastrophe depends primarily on decisions we make right now in developing, regulating, and deploying these technologies that will reshape civilization forever.
Critical Juncture: We stand at a pivotal moment. The next 3-5 years will likely determine whether AGI becomes humanity's greatest achievement or greatest threat. Choices made by researchers, companies, and governments today shape the future of human civilization itself.
Continue the AI Evolution Journey
Complete AI Evolution Series Navigation:
- Part 1: The Evolution of AI - Overview
Foundation concepts and comprehensive timeline - Part 2: Artificial Narrow Intelligence (ANI)
Current specialized AI systems and capabilities - Part 3: Artificial General Intelligence (AGI) ← You are here
Human-level cognitive abilities across diverse tasks - Part 4: Artificial Super Intelligence (ASI)
Beyond human intelligence and the ultimate frontier
Example Implementation
# Example: Model training with security considerations
import numpy as np
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestClassifier
def train_secure_model(X, y, validate_inputs=True):
"""Train model with input validation"""
if validate_inputs:
# Validate input data
assert X.shape[0] == y.shape[0], "Shape mismatch"
assert not np.isnan(X).any(), "NaN values detected"
# Split data securely
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(
X, y, test_size=0.2, random_state=42, stratify=y
)
# Train with secure parameters
model = RandomForestClassifier(
n_estimators=100,
max_depth=10, # Limit to prevent overfitting
random_state=42
)
model.fit(X_train, y_train)
score = model.score(X_test, y_test)
return model, score